[Scale]
오브젝트의 크기. 확대/축소 할 수 있는 기능이다. 지구와 성 등 보다 큰 모델을 필요하다고 가정하면, 모델을 만들 때 처음부터 거대한 모델을 만들 필요 없이 작게 만들어 유니티에 와서 Scale을 통해 크기를 늘리면 된다.
[Position]
오브젝트의 위치. 이동과 관련되어 있는 기능이다.
거리 = 시간 * 속력
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class PlayerController : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField]
private float _speed = 10.0f;
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.W))
transform.position += new Vector3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f) * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.S))
transform.position -= new Vector3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f) * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.D))
transform.position += new Vector3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f) * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.A))
transform.position -= new Vector3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f) * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
}
매 프레임마다
1. W키를 누르는 중이라면 현재 위치로부터 한 프레임동안 Vector3(0.0f, 0.0f, Time.deltatime * _speed) 만큼 더 이동한다.
방향(벡터) 👉 Vector3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f)
- Z 축 positive 방향이니 Vector3.forward 와 방향이 같다.
거리(스칼라) 👉 시간 X 속력 = Time.deltaTime * _speed
- 프레임간의 간격 시간동안 _speed 크기만큼 이동한다.
2. S키를 누르는 중이라면 현재 위치로부터 한 프레임동안 -Vector3(0.0f, 0.0f, Time.deltatime * _speed) 만큼 더 이동한다.
방향(벡터) 👉 -Vector3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f)
- Z 축 negative 방향이니 Vector3.back 와 방향이 같다.
거리(스칼라) 👉 시간 X 속력 = Time.deltaTime * _speed
- 프레임간의 간격 시간동안 _speed 크기만큼 이동한다.
3. D키를 누르는 중이라면 현재 위치로부터 한 프레임동안 Vector3(Time.deltatime * _speed, 0.0f, 0.0f) 만큼 더 이동한다.
방향(벡터) 👉 Vector3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
- X 축 positive 방향이니 Vector3.Right 와 방향이 같다.
거리(스칼라) 👉 시간 X 속력 = Time.deltaTime * _speed
- 프레임간의 간격 시간동안 _speed 크기만큼 이동한다.
4. A키를 누르는 중이라면 현재 위치로부터 한 프레임동안 -Vector3(Time.deltatime * _speed, 0.0f, 0.0f) 만큼 더 이동한다.
방향(벡터) 👉 -Vector3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
- X 축 negative 방향이니 Vector3.Left 와 방향이 같다.
거리(스칼라) 👉 시간 X 속력 = Time.deltaTime * _speed
- 프레임간의 간격 시간동안 _speed 크기만큼 이동한다.
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.W))
transform.position += Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.S))
transform.position += Vector3.back * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.D))
transform.position += Vector3.right * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.A))
transform.position += Vector3.left * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}위와 같이 변경하여 사용할 수 있다.
[World 좌표계 / Local 좌표계]
현재 Player오브젝트를 Y 축으로 45 회전한 상태다.
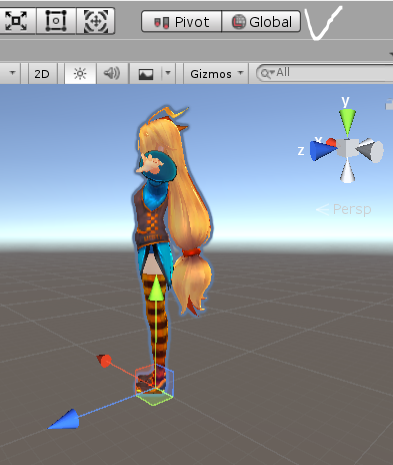
왼쪽 사진은 World 좌표계, 즉 Global 을 기준으로 한 Player오브젝트의 좌표계를 나타낸다.
플레이어는 월드 좌표계의 Y 축을 기준으로 45 도 회전한 곳을 바라보고 있지만 이와 상관없이 절대적인 월드 세상 기준에서의 ‘앞’방향은 파란색 화살표(Z축 Positive)임을 알려준다.
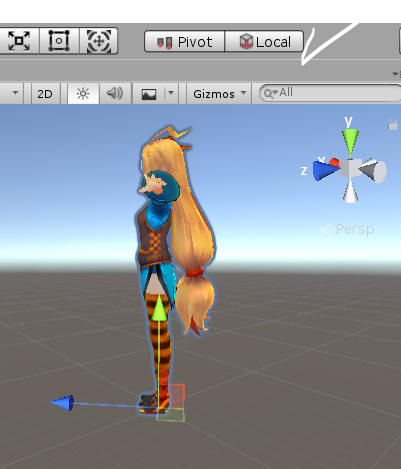
오른쪽 사진은 Local 좌표계를 기준으로 한 Player오브젝트의 좌표계를 나타낸다.
플레이어는 월드 좌표계의 Y 축을 기준으로 45 도 회전해 있지만 플레이어 기준에선 앞 쪽 방향이 현재 플레이어가 바라보고 있는 월드 좌표계의 Y 축을 기준으로 45 도 방향이기 때문에, 이 방향이 Local 좌표계로선 플레이어의 ‘앞’방향이다. 플레이어가 바라보고 있는 방향이 앞쪽임을 나타내는 파란색 화살표(Z축 Positive)임을 알 수 있다. 또한 로컬 좌표계는 주로 모델러 분들이 사용한다. (앞/뒤 만 있는 상황에서 제작한다고 생각하면 쉽게 이해할 수 있다.)
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.W))
transform.position += transform.TransformDirection(Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.S))
transform.position += transform.TransformDirection(Vector3.back * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.D))
transform.position += transform.TransformDirection(Vector3.right * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.A))
transform.position += transform.TransformDirection(Vector3.left * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
}
TransformDirection(Vector3) 함수
인수로 받은 좌표 Vector3 를, 함수를 호출한 오브젝트의 Vector3 로컬 좌표계 기준에서 월드 좌표계 기준으로 방향만 변환하여 이를 리턴해준다. (벡터 길이는 변하지 않는다.)
InverseTransformDirection(Vector3) 함수
인수로 받은 좌표 Vector3 를 월드 좌표계 기준에서 로컬 좌표계 기준으로 방향만 변환하여 이를 리턴해준다.
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.W))
transform.Translate(Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.S))
transform.Translate(Vector3.back * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.D))
transform.Translate(Vector3.right * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.A))
transform.Translate(Vector3.left * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
}
Translate 함수
Local 좌표계를 기준으로 인수로 들어온 Vector3 만큼 이동한다. Space.World를 두 번째 인수로 넘기면 World 좌표계를 기준으로 이동시킬 수 있다.
[Vector3]
// Vector3 구현해보기 😎
struct MyVector
{
public float x;
public float y;
public float z;
public float magnitude { get { return Mathf.Sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z); } }
public MyVector normalized { get { return new MyVector(x / magnitude, y / magnitude, z / magnitude); } }
public MyVector(float x, float y, float z)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
}
public static MyVector operator + (MyVector a, MyVector b)
{
return new MyVector(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y, a.z + b.z);
}
public static MyVector operator - (MyVector a, MyVector b)
{
return new MyVector(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y, a.z - b.z);
}
public static MyVector operator * (MyVector a, MyVector b)
{
return new MyVector(a.x * b.x, a.y * b.y, a.z * b.z);
}
}
Vector3는 3개(x, y, z)의 float 을 원소로 가지기 때문에 3 가지의 값이 필요한 곳이라면 Positiom, Scale, Rotation 등등 여러가지 곳에서 사용이 가능하다.
[Vector3의 용도]
1️⃣ 위치 벡터 를 표현
말 그대로 어떤 좌표. 상태.
2️⃣ 방향 벡터 를 표현
예를 들어 A 위치 벡터에서 B 벡터 만큼 더해서 C 위치 벡터가 된다는 의미에 주목해 보면, B 벡터는 A 위치 벡터가 C 위치 벡터로 향하는 '방향 벡터'가 된다. X 방향으로, Y 방향으로, Z 방향으로 이만큼만 이동 해 보아라 이런 뜻이니까!
void Start()
{
MyVector to = new MyVector(10.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
MyVector from = new MyVector(5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
MyVector dir = to - from; // (5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); 👉 방향의 크기(거리)는 5, 실제 방향은 오른쪽
}
목적지 위치 벡터 - 출발지 위치 벡터 = 방향 벡터
👉출발지로부터 목적지로 향하는 방향을 의미하게 된다.
방향 벡터
1️⃣ 방향에 대한 크기(스칼라). 즉, 방향에 대한 거리를 알 수 있다
magnitude
public float magnitude { get { return Mathf.Sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z); } }
2️⃣ 실제 방향을 알 수 있다. 크기가 1 이라 오직 방향에만 무게를 둔 단위 벡터(forward, back, left, right 와 같이) 각 요소를 크기(magnitude)로 나눠주면 된다
normalized
public MyVector normalized { get { return new MyVector(x / magnitude, y / magnitude, z / magnitude); } } void Start()
{
MyVector to = new MyVector(10.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
MyVector from = new MyVector(5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
MyVector dir = to - from;
dir = dir.normalized;
MyVector newPos = from + dir * _speed;
}
[Rotation]
오브젝트의 회전 값.
회전 값을 절대적으로 설정할 때 👉 eulerAngles
유니티에선 Transform 의 rotation 은 Vecotr3 가 아닌 Quaternion 이다.(x,y,z,w 이렇게 4개의 값이 필요) 따라서 Vector3 형태로 X, Y, Z 축 이렇게 3 개의 회전 값으로 회전 값을 설정하고 싶다면 eulerAngles를 사용해야 한다.
transform.eulerAngles = new Vector3(0.0f, _yAngle, 0.0f); // Y 축으로 _yAngle 각도 만큼 회전한다.
eulerAngles 👉 오일러 각도의 회전 값을 나타내며 Vector3 를 사용해 회전 값을 설정할 수 있다.
📢 주의 사항
밑에 코드와 같이 절대적인 회전 Vector3 값으로 설정하는 것이 아닌, 이만큼 더 회전해라! 하는 델타 값 의미로 eulerAngles에 Vector3를 더하고 빼주는건 안된다. 오일러 각도는 360도를 넘어가면 값의 계산에 실패하기 때문에 eulerAngles를 얼만큼 더 회전할지의 델타 회전값으로 사용하는 것은 권장하지 않는다.
transform.eulerAngles += new Vector3(0.0f, _yAngle, 0.0f); // '+=' ❌❌❌
회전 값을 상대적으로 설정할 때 👉 Rotate
eulerAngles로는 얼만큼 더 회전할지의 델타 회전값으로 사용하는 것이 불가능 하기 때문에, 얼만큼 더 회전할지의 델타 회전 값을 설정해주는 것은 Rotate 함수를 사용하여야 한다. 현재 회전값으로부터 인수로 넘기는 Vector3 만큼 더 회전한다. eulerAngles와 비슷하게 Vector3를 인수로 받는다. (내부적으로 eulerAngles만큼 더 회전시킨다.)
transform.Rotate(0.0f, Time.deltaTime * _speed, 0.0f);
[쿼터니언 함수 소개]
Quaternion.Euler(Vector3)
👉 인수로 받은 Vector3 를 쿼터니언으로 변환하고 이를 리턴해준다. Euler() 함수로 Vector3를 쿼터니언으로 변환하면, 쿼터니언 타입은 transform.rotation에 할당이 가능해진다.
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Euler(new Vector3(0.0f, _yAngle, 0.0f));
Quaternion.LookRotation()
👉 우리가 원하는 방향을 쳐다 보는 회전 값을 쿼터니언으로 리턴한다. Vector3를 인수로 넘기면 인수로 넘긴 Vector3의 방향을 쳐다보는 회전값(쿼터니언)을 리턴한다.
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.S))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.back);
}S키를 누르면 Vector3.back 방향을 바라보는 회전 상태를 쿼터니언으로 반환한다. 이를 transform.rotation으로 설정하면 그 방향으로 오브젝트가 회전할 것이다.
Quaternion.Slerp(Vector3 a, Vector3 b, float t)
👉 A에서 B 까지 0.0 ~ 1.0 퍼센트 비율로 보간. Lerp 와 같다!
🎈 Lerp와는 뭐가 다른걸까? 🤯
Lerp 👉선형 보간법
Slerp 👉구면 선형 보간법, 회전이나 방향을 보간할 때 주로 쓰인다.
좀 더 부드럽게 회전시킬 수 있다. A 벡터와 B 벡터 사이를 t 퍼센트로 보간한 결과를 쿼터니언으로 리턴한다.
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.forward), Time.time * speed);
[WASD 이동하면서 자연스럽게 그 쪽으로 회전하는 코드]
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.W))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.forward), 0.2f);
transform.Translate(Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.S))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.back), 0.2f);
transform.Translate(Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.D))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.right), 0.2f);
transform.Translate(Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.A))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.left), 0.2f);
transform.Translate(Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed);
}
}
WASD 키를 누를 때마다 해당하는 방향으로 회전한다. 따라서 Translate 으로 이동을 할 때는 상대적인 방향으로 이동 하기 때문에, Translate 의 인수로 넣어주는 Vector3의 방향은 Vector3.forward 가 되야 한다.
👉 따라서 쿼터니언의 LookRotation 함수 덕에 향하고자 하는 방향으로 회전을 먼저 했기 때문에 자기 자신의 입장에선 상대적으로 그저 앞으로 가면 되기 때문이다. 이처럼 회전과 이동을 병행할 땐 방향, 절대적, 상대적 방향을 잘 생각해야 한다.
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.W))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.forward), 0.2f);
transform.position += Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.S))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.back), 0.2f);
transform.position += Vector3.back * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.D))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.right), 0.2f);
transform.position += Vector3.right * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.A))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.left), 0.2f);
transform.position += Vector3.left * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
}
Translate 을 썼을 때는 Slerp를 통해 보간 중에도 상대적인, 자기 기준에서의 forward 방향으로 계속 이동을 했어서 조금 부자연스러웠었다. 따라서 이렇게 transform.position += Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed; 그냥 절대적인 좌표로 위치를 설정해주면 더 자연스러워질 것이다. Translate 과 다르게 절대적인 좌표를 대입하기 때문에 모두 Vector3.forward 였었던 것과 달리 각각 4 가지의 절대 방향을 다시 설정해주었다.
[Input Manager]
Update() 함수내에서 직접 입력이 들어오는 것을 관리하는건 비추다. 이유는 아래 서술한다. 따라서 공용으로 사용할 수 있는, 입력을 총괄 관리하는 Input Manager 같은 것을 따로 만들면 좋다.
예를들어 게임에 입력 받을 수 있는 키보드 Key 종류가 예를 들어 100개라면, Update() 함수내에서 입력을 관할 했을 때 매 프레임마다 매번 100개의 Key 입력을 전부 검사해야 하므로 비효율적이며, 코드를 수정하기도 어렵다. 따라서 Update 문에 넣지 않고 공용으로 이곳 저곳에서 사용될 수 있는 입력 검사 관할 함수로서 따로 빼는게 좋다. 이렇게 할 경우 디버깅도 쉬워지고 수정도 쉬워진다.
InputManager.cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using System;
public class InputManager
{
public Action KeyAction = null;
public void OnUpdate()
{
if (Input.anyKey == false) // 어떤 키던 간에 false 면 그냥 return
return;
if (KeyAction != null)
KeyAction.Invoke();
}
}
디자인 패턴 중 일부인 리스너 패턴이 사용된다. 또한 InputManager.cs는 모노비헤이비어를 사용하지 않고 일반 C# 스크립트로 구현했다.
OnUpdate() 👉 어떤 입력이든 입력이 들어온게 아예 없다면 그냥 함수를 실행하지 않고 return한다. KeyAction 액션에 등록된 함수가 있다면 실행시킨다.
if (KeyAction != null)
KeyAction.Invoke();
Managers.cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Managers : MonoBehaviour
{
static Managers s_instace;
static Managers Instance { get { Init(); return s_instace; } }
InputManager _input = new InputManager();
public static InputManager Input { get { return Instance._input; } }
void Start()
{
Init();
}
void Update()
{
_input.OnUpdate();
}
static void Init()
{
if (s_instace == null)
{
GameObject obj = GameObject.Find("@Managers");
if (obj == null)
{
obj = new GameObject { name = "@Managers" };
obj.AddComponent<Managers>();
}
DontDestroyOnLoad(obj);
s_instace = obj.GetComponent<Managers>();
}
}
}
Managers.cs 인스턴스(Instance)는 싱글톤으로 설정했다. 따라서 Managers.cs 안에서 InputManager.cs 타입의 _input 인스턴스를 생성했으니 이제 _input는 Managers.cs의 멤버가 된다. 이로인해_input이 Managers.cs에 속한 멤버이니 InputManager.cs 도 마찬가지로 싱글톤인게 보장 될 수 있다.
Input는 이 Managers.cs 인스턴스의 _input을 불러오는 프로퍼티다. (싱글톤 불러다 주는 static 함수 같은 역할. 프로퍼티로 구현한 것 뿐.)
get { return Instance._input; }
Update() 👉 유니티 이벤트 함수이다. 따라서 매프레임마다 _input.OnUpdate()을 실행시켜주기만 하면 땡이다. InputManager.cs의 OnUpdate() 함수 여기서는 또 KeyAction만 Invoke 시키는 일을 한다.
PlayerController.cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class PlayerController : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField]
float _speed = 10.0f;
void Start()
{
Managers.Input.KeyAction -= OnKeyboard;
Managers.Input.KeyAction += OnKeyboard;
}
void OnKeyboard()
{
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.W))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.forward), 0.2f);
transform.position += Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.S))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.back), 0.2f);
transform.position += Vector3.back * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.D))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.right), 0.2f);
transform.position += Vector3.right * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.A))
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation, Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.left), 0.2f);
transform.position += Vector3.left * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
}
}
InputManager.cs의 KeyAction에 플레이어의 입력을 검사하는 함수인 OnKeyboard()을 등록해둔다. 이렇게 설정하게 될경우 Managers.cs와 InputManager.cs 에서는 KeyAction에 어떤 함수들이 등록되어 있는지 알 필요 없이 그저 실행만 해줄 뿐이다. 실행은 매니저에게만 맡기는 것이다.
이로인한 장점은 입력 키에 대한 어떤 추가 삭제가 있을시 코드 수정을 할 필요가 없다. PlayerController.cs의 OnKeyboard() 내용만 수정하면 될 뿐이다. 그리고 이를 그저 KeyAction 등록만 해두면 된다. 👍
void Start()
{
Managers.Input.KeyAction -= OnKeyboard;
Managers.Input.KeyAction += OnKeyboard;
}
PlayerController.cs 입장에서는 플레이어의 입력을 검사하는 함수인 OnKeyboard() 내용만 작성하고 이를 KeyAction에 등록만 해두면 될 뿐이다. 실행은 Managers.cs가 해준다.
그리고 이벤트를 등록하기(+=)에 앞서 삭제(-=)를 한번 시켜주는 이유는 실수를 방지할 수 있다. 실수로 다른 곳에서 OnKeyboard() 를 이미 등록했다면 두 번 등록이 되는거라 OnKeyboard() 이 두번 호출되게 된다. 그러므로 혹시나 실수했을 경우를 대비해 한번 빼고 시작해주는 것.
InputManager.cs 에서 KeyAction를 Invoke 시킬 때, 등록된 함수인 OnKeyboard()가 PlayerController.cs에서 등록되었으므로 이를 기억하고 PlayerController.cs 객체의 OnKeyboard() 함수를 호출하게 된다.
'공부 > 인프런 - Rookiss' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Part 3-4-1. Collider, Collision, Trigger (0) | 2023.08.17 |
|---|---|
| Part 3-3-1. Prefab (프리팹), Resource Manager (0) | 2023.08.17 |
| Part 3-1-1. 싱글톤 (0) | 2023.08.11 |
| Part 3. 유니티 엔진 (0) | 2023.08.10 |
| Part 2-6-1. A* 길찾기 알고리즘 (0) | 2023.08.10 |